URL (Uniform Resource Locator) – How it Works & Overview

We all heard about the URL, but do you exactly know how it works? If your answer is a big NO, then don’t worry. We help you to find out.
So, in this post, we have covered all the information related to the URL (Uniform Resource Locator)? How it works, overview and history of the development.
What is the URL?

URLs are the language of browsing the internet, which you do every day. By definition, URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a specified address of any file or web site over the internet.
Therefore, any data whether it is an image, page, sound file, or hypertext— all have a fundamental specific address that is on the web.
For example, the URL of our homepage is https://etipsguruji.com/.
The URL has an Http protocol and a TLD name (domain name) etipsguruji.com.
Hence, if you want to open our website, you have to type our URL in the address box. And by default, all web pages are first redirected through Http then pass-over to https (in case of SSL).
However, if you directly put the https then the server redirects directly to the security patched server.
History and Development of URL
While talking about its development, it was brought to the world by Tim Berners-Lee in 1994. He developed an organized way to provide a unique locational address to all web pages (or resources) that were available over the internet.
Therefore, if they have that unique address then all the resources were easily located. But at that time only IP address is used to locate data but now, TLD (the domain name) can be used to interpret a location.
Tim Berners Lee and his team members had created a bunch of HTML pages over the World Wide Web (WWW) using standard language and hyperlinks with it. After that, they combined them both. Due to this, it became faster.
Did you know? Tim Berners Lee invented the World Wide Web(WWW), HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), and HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol).
History and Development of URL

For obvious, we need a URL to identify the address of documents and other resources on the web. It consists of multiple parts – including a protocol and domain name which we discuss later in this post.
The URL’s different parts are responsible to retrieve resource data as per the request of a browser. And the most important thing, it makes you remember the address of the requested site (easy domain name).
How does the URL Work?

Uniform Resource Locator (that has a domain name) has been specifically one purpose i.e. we people, can easily remember it. But a computer (or machines, server) needs full details to find the correct website.
Therefore, when you type the URL of a website, then the browser requests the server (DNS-Domain Name Server). And with the help of this, it converts that URL into its corresponding IP.
Then the server interacts with the browser and sends information into data pockets and you get what you were looking for.
Did you know? Not every website has static URLs that often get changed with time but as they are dynamic in nature, they are very unpredictable to users. That’s why we’re using static URLs—that is always the same—and also very easy to recall.
Parts of Uniform Resource Locator
While talking about its part, it has a hierarchical sequence of four elements which are as follows;
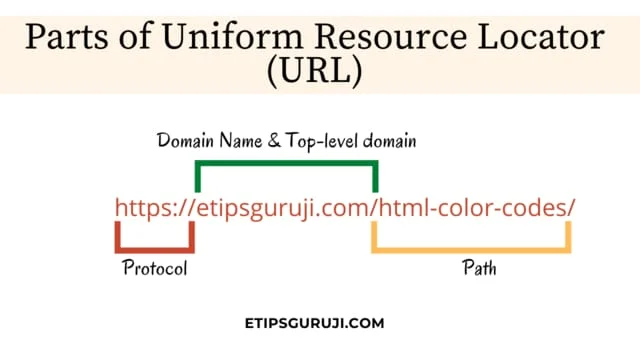
1. Protocol or Scheme
The first part of the URL is the protocol identifier which indicates which protocol to use for transferring data from server to browser.
There are majorly two types of protocol for an online website— Http and Https. However, there are other protocols that a web browser is compatible with, which includes FTP, UDP, etc.
How do I find which protocol is being used? The majority of the protocols have a colon followed by two slashes, and then the domain name (or IP address).
2. Host or Domain Name
A domain name tells, from which DNS server the data is going to fetch out. You could call it the destination location where all data files are stored in their particular sub-links and directories.
However, the location could be a domain name or IP address on a computer on which the resources are located. But both works in the same way— all data files are in their sub-directories with their common domain or Ip address.
While considering the common scenario with the domain name, there could be Second-level Domain, Top-level Domain, and Subdirectories(categories).
3. Path
In case you want to visit our website’s home page, you just need to type https://etipsguruji.com/. However, if you want to visit a specific page or post you need its own URLs.
For example, if you want to read a post on “HTML Color Code” it has its own URL with sub-links. Therefore, the part after the TLD (domain) is known as the path.
There are several analog parts of the path URL that are usually of two forms.
Related Articles:
- How to block a website on Chrome on Desktop, Android & IOS
- What is Cable modem- How it Works, Advantages & Disadvantages
- 5G Technology – How it Works, Features, Advantages & Disadvantages
- Server- Types, Purpose, Advantage & Disadvantage
Query String
If you search a query on the website’s search tab, then this time, the domain name has a question mark (?) and then query. And this type of path, calls to be a query string.
However, in some cases, before the query, they have an equal sign ‘=’ which are separated from each other by an ampersand (&).
Fragment ID or Hash (#)
A fragment ID represents a part of a page, which is usually the heading or subheading of the post. They appear at the end of a name URL with a hash(#) that separates the name path with the internal linked page element.
This is how Fragment ID looks: https://etipsguruji.com/http/#what_is_http
Port
There are like the USB cable that can transfer data from your mobile to computer (or other devices) but here it connects the browser to the locational server.
These are some common ports that you may encounter with.
Types of Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
There are various types of Uniform Resource Locator, some of which are listed below:
Messy URLs
These are a total mess because they are very hard to remember as they have a lot of numbers and letters which are normally randomly assigned. These URLs are generally seen in short linking URLs, drive file URLs, etc.
This is an example of a messy URL: http://www.example.com/wxbtj7832hjksd/
Dynamic URLs
Dynamic URLs are the result of a database query with characters like ?, %, =, +, etc. They are generally used by the users to seek out their desired data.
Static URLs
For these URLs, a specific URL is hard-wired by HTML coding for web pages. And the same URL never changes, no matter what the user requests.
A static URL is a very dangerous URL that is generally used in the phishing scams. These URLs are made to look original but they redirect it to some malicious websites.
Absolute URLs
When the full URL of a web resource is written in context, it is called the absolute URL. This type of URL itself represents what the context is all about.
Example: https://tipsguruji.com/What-is-http;
Here, the post URL itself represents what the page tells.
Relative URLs
When the full syntax of the URL is missing and doesn’t clearly state the specific type of the page, then they are relative URLs. They become popular nowadays because they are the base of the URL shortener websites.
Miscellaneous Topic related to URL
Secure URLs

From now, you have an idea what are secure URLs— they are just the secure version of Http— that is represented by Https. They are now becoming an important factor in the digital world especially for the website owners because it gives trust to their users.
Also, Google and many browsers alarm users for visiting a non-secure version of the web. There are many companies that provide secure Http access. And one of the widely used secure Http is the Let’s Encrypt SSL.
URL Shortening
If you want to hide the main URL of your website then you can use a link shortener website. There are various websites that have their own shortener links. For example, t.co (for Twitter) and lnkd.in (for LinkedIn).
One another reason why many users use URL shortener link is to cut down the long string of URLs,
Conclusion
At last, we had sum up all the details about URL including its parts, types, and basic syntax. So, through this post, we have provided you with the various details of URL, and most importantly how URL works.
We hope you like this piece of information helpful. And if you want more beneficial articles like this then check our technology category list.
General FAQ
Is a URL the same as a domain name?
Ans. Surprisingly, the answer is no. But the terms can be interchangeable. A domain name is part of a URL and the URL is the whole thing including top-level domain, sub-domain, and page subdirectories path.
What are the three main parts of an URL?
Ans. The three main parts are the protocol, domain name (along with top-level domain), and the path.
What is URL encoded data?
Ans. This is a method for converting URL characters into a widely accepted format by web servers and browsers.
What is a URL query string?
Ans. A query string is a part of a URL that has a definite value based on specified parameters which are added to the tail of an URL to specify the query.

