Flash Memory – How it Works, Types, Applications, Advantages

Flash memory is used in various consumer devices, including data center servers, storage and network technologies, USB flash memories. This post will discuss in brief about what is flash memory, how it works, its types, applications, advantages and disadvantages.
What is Flash Memory?
Flash memory is a type of erasable read-only memory (EEPROM) that erases and overwrites block data for quick and energy-efficient access and overwriting. It is not volatile. It works without active power. Flash memory is technically read-only (ROM), but, unlike traditional ROMs, it can be read by modification.

How does flash memory work?
The flash cells are present in every chip. And each chip is integrated into the memory, that memory is called flash memory.It stores data with circuits that do not use conventional electromechanical methods.
The process is as follows.
- The current flows through a transistor between the source (electrical input) and the drain (electrical output) of each cell.
- The transistor acts as an ON / OFF switch or gate to control the flow of current.
- An “on” transistor slides electrons through a battery that stores the unit in binary code.
- An “off” transistor blocks the first and stores zero.
When the power is turned off, volatile memory, such as RAM (Random Access Memory), resets all ports to zero and clears all stored data. However, ROM (with flash memory) works by adding a second port to each cell (also called a “floating port”).
When an electron passes through the transistor in on state, some electrons attach themselves to the floating gate, regardless of whether not they are getting energized. All types of programmable read-only memory (PROM) lose their electronics. An electrically erasable ROM (EEPROM) ensures that the shutter stops electrons only if the user sets the transistor to zero by applying a specific negative voltage to the screen.
What is Flash Memory Types

There are two main types
(i) NOR and
(ii) NAND
NOR
The name represents the type of logical element used for each type. A logical element is a group of transistors that work together to perform an “if-then” operation to achieve the desired result. The structure of the logical element determines the output that produces the possible input.
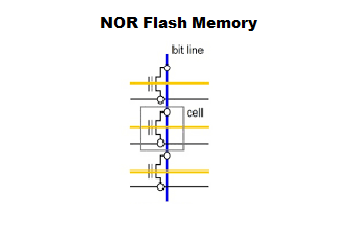
NOR can read and read more accurately and read faster than NAND, but the price per byte is rising. Users mainly choose the NOR flash to run the code.
NAND
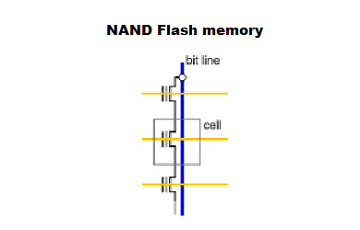
NAND can access memory block by block, but not slow reading bytes, but cheaper than NOR. Suitable for storing regularly updated files.
Applications
Flash memory technology has become the optimal storage medium for a wide range of industrial and household devices.
Home Appliances
- laptop
- Digital camera
- Personal terminal (PDA)
- Mobile phone
- Global Positioning System (GPS)
- Electronic tools
- For example, a music player.
- TV decoder
- MP3 player
- a computer
Related Articles:-
- Full Form of Computer- Its Generations, Parts and Types
- How to block a website on Chrome on Desktop, Android & IOS
- What is Cable modem- How it Works, Advantages & Disadvantages
Industrial Devices

- Safety system
- Military system
- Embedded computer
- SSD drive
- Network and Communications Products
- Wireless device
- Distribution Management Products (Handheld Scanners, etc.)
- Medical supplies
Related Articles
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Definition, Need, Working Mechanism
- CBR file- Steps to Convert and Open in Various Devices
Advantages
- Compared to traditional hard drives, reading and writing are faster.
- Small size
- Hard to hurt
- The lower the storage capacity, the cheaper it is than a regular disk.
- Less power consumption than traditional hard drives.
Disadvantages
- Flash cells have a limited number of write and erase cycles before they stop working.
- Most flash drives do not have a write protection mechanism
- Smaller devices (like flash drives) get lost easily
- For high-capacity storage, the current cost per GB is much higher than that of traditional hard drives.
- For use on a flash drive, a particular version of the program may be required to prevent premature wear of the drive.
General FAQs
What are the advantages of flash memory?
Flash memory has the following characteristics: Data can get saved even when the power is getting turned off. Since it is not volatile, it does not require energy to keep fit. The transfer speed is high, therefore the read and write speeds are higher than those of conventional hard disks.
SSD vs Flash RAM vs Hard drives?
SSDs are much faster than hard drives because they use integrated circuits. SSDs use a special type of storage scheme called non-volatile RAM (NVRAM) to store data even when the computer is turned off, all of this is there.
Is Flash memory faster than RAM?
Flash memory is mainly used for archiving, but RAM (Random Access Memory) counts data obtained from archiving. In fact, it is faster than flash memory and alternative storage, such as RAM, hard drive, or magnetic tape … Unlike RAM, flash memory is not volatile and allows you to store data without power.
ALSO READ

